Describe How Viruses and Prions Can Alter Cell Functions.
After entering a cell they alter something about its protein formation. This is a symptom of _____.

Blessings In Disguise Biological Benefits Of Prion Like Mechanisms Trends In Cell Biology
Viroids do not however manufacture any proteins and they only produce a single specific RNA molecule.

. Viroids are plant pathogens. PrPsc This is the disease-causing prion and is resistant to proteases. Up to 24 cash back VIROIDS PRIONS Viroids Naked strands of RNA not covered by a capsid Must infect a host cell to reproduce Prions Proteinaceous infectious particles When in contact with prion a normal protein will change shape altering function TSEs transmissible spongiform encephalopathies.
Some infected cells such as those infected by the common cold virus known as rhinovirus die through lysis bursting or apoptosis programmed cell death or cell suicide releasing all progeny virions at once. The virus surfs along the fluid surface of the cell and eventually the viral fusion proteins bind to receptor molecules on the cell membrane. PrPc These prion proteins are found on the cell membrane and play an important role in cell signalling and cell adhesion.
Then fully formed viruses assemble. The phage attaches to the cell membrane and injects viral DNA or RNA into the living host cell. An apple tree has yellow splotches on the leaves.
The prion protein is found in the neurons of healthy animals PrPC or Prion Protein Cellular with a particular secondary structure. The two isoforms of prions are. Prions so-called because they are proteinaceous are infectious particlessmaller than virusesthat contain no nucleic acids neither DNA nor RNA.
A virus must use its host-cell processes to replicate. 1 the tumor virus may introduce and express a so-called transforming gene in the cells or 2 the tumor virus may alter the expression and or coding capacity of preexisting cellular genes. These changes called cytopathic causing cell damage effects can change cell functions or even destroy the cell.
They do not have a capsid or outer envelope but like viruses can reproduce only within a host cell. The infected cell mistakenly copies the phage DNA or RNA whichever nucleic acid the phage possesses. These changes called cytopathic effects can change cell functions or even destroy the cell.
More research is being carried out to discover its functions. Injected phage nucleic acids contort into a circle inside the cell. Undergoing shape changes and creating channels in the host cell membrane is an alternative method of cell penetration used by naked viruses.
Propose ideas for the development of drugs that could stop viral replication cycles. Prions attack nerve cells producing neurodegenerative brain disease. Like the lytic cycle in the lysogenic cycle the virus attaches to the host cell and injects its DNA.
Possible Mechanisms by Which Viruses Cause Cancer. The pathogenic form PrPSC or Prion Protein Scrapie has a different secondary structure and is capable of converting the PrPC into the pathogenic form. After development of a malignant phenotype the.
A virus must use cell processes to replicate. Describe how viruses and prions can alter cell functions. Up to 24 cash back 1.
Draw a diagram of a virus and label the parts. Some infected cells such as those infected by the common cold virus known as rhinovirus die through lysis bursting or apoptosis programmed cell death or cell suicide releasing all progeny virions at once. There are two general patterns by which cell transformation may be accomplished.
Steps of Virus Infections. These changes called cytopathic effects can change cell functions or even destroy the cell. Due to prions Mad cow disease.
It affects the confirmation of PrPc and changes it. These elongated fibrils green are believed to be aggregations of the protein that makes up the infectious prion. Describe how viruses and prions can alter cell function.
The viral replication cycle can produce dramatic biochemical and structural changes in the host cell which may cause cell damage. Viruses initially stick to cell membranes through interactions unrelated to fusion proteins. Using the hosts cellular metabolism the viral DNA begins to replicate and form proteins.
65 Cultivation and enumeration of viruses. Small single-stranded circular RNA particles that are much simpler than a virus. Viruses and prions have the ability to reproduce.
Lytic Cycle The host cell makes many copies of the viral RNA or DNA. The viral replication cycle can produce dramatic biochemical and structural changes in the host cell which may cause cell damage. Accumulation of the pathogenic form causes destruction of brain and nervous tissue leading.
These changes called cytopathic causing cell damage effects can change cell functions or even destroy the cell. Mechanisms of Oncogenic Transformation. Lysogenic Cycle The viral DNA inserts or integrates into a chromosome in a host cell.
If only binding occurred the two membranes would remain distinct. Prions are virus-like organisms made up of a prion protein. Compare and contrast the replication of a herpes simplex virus with a human immunodeficiency virus.
Mad cow symptoms include glazed eyes and uncontrollable body tremor. Viral proteins bind host cell tumor suppressor proteins Carry oncogene into cell and insert it into host genome Altered cell regulation Insertion of promoter or enhancer next to cellular oncogene. The Role of Viruses in Cancer Cell division is under strict genetic control Genes dictate that some cells can no longer divide at all Cells that can divide are prevented from unlimited division Genes for cell division turned off or genes inhibiting division turned on Neoplasia Uncontrolled cell division in multicellular animal.
Prions so-called because they are proteinaceous are infectious particlessmaller than virusesthat contain no nucleic acids neither DNA nor RNAHistorically the idea of an infectious agent that did not use nucleic acids was considered impossible but pioneering work by Nobel Prize-winning biologist Stanley Prusiner has convinced the majority of biologists that such. These viruses break or lyse the cell and spread to other cells to continue the cycle. The copied nucleic acids organize as phages.
Prions and viroids are pathogens agents with the ability to cause disease that have simpler structures than viruses but in the case of prions still can produce deadly diseases. Steps of Virus Infections. Historically the idea of an.

Cell Biology Of Prions And Prionoids A Status Report Trends In Cell Biology

Yeast Prions Are Infectious A A Sexual Cross Of Prion And Download Scientific Diagram
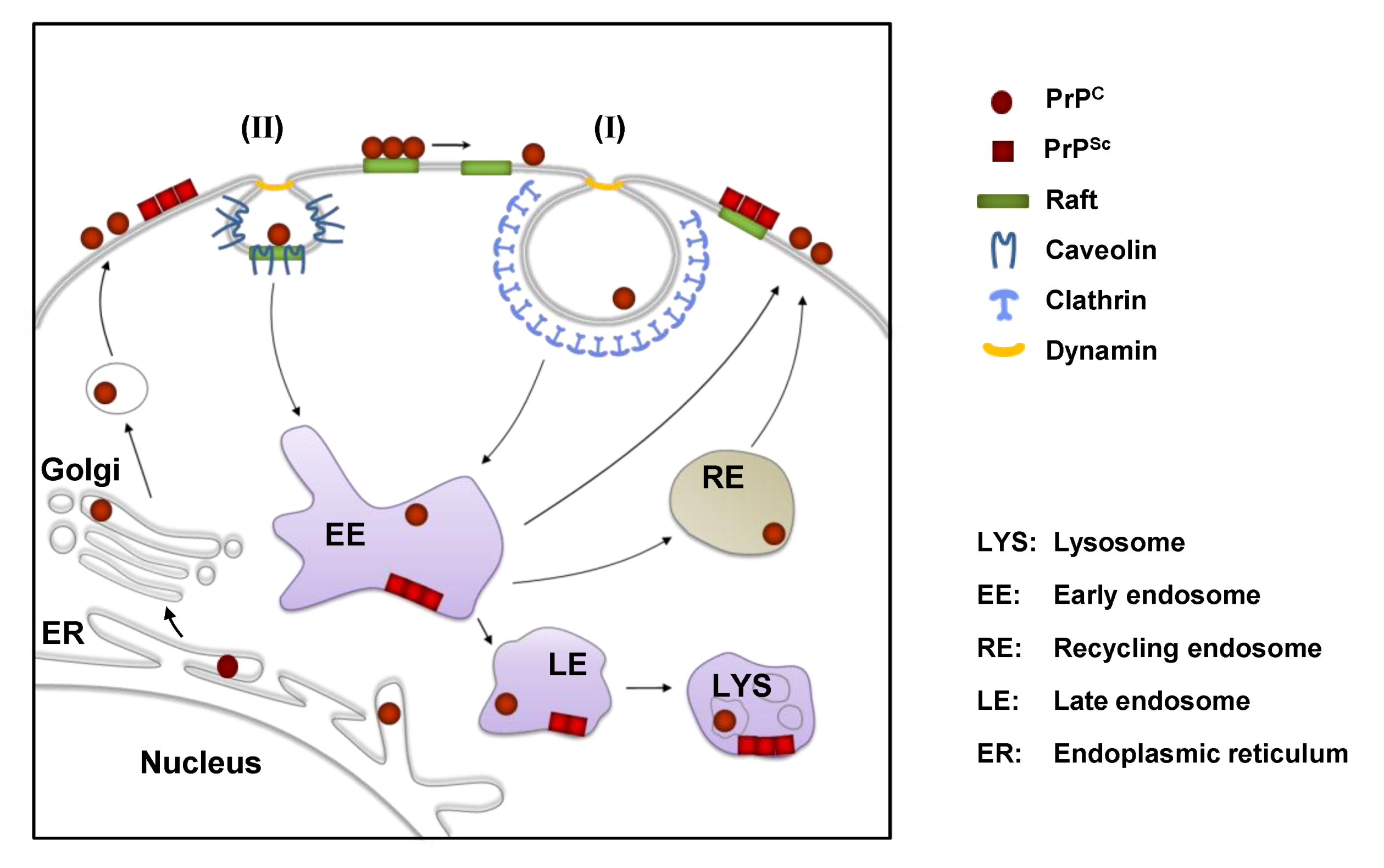
Viruses Free Full Text Cellular Aspects Of Prion Replication In Vitro Html
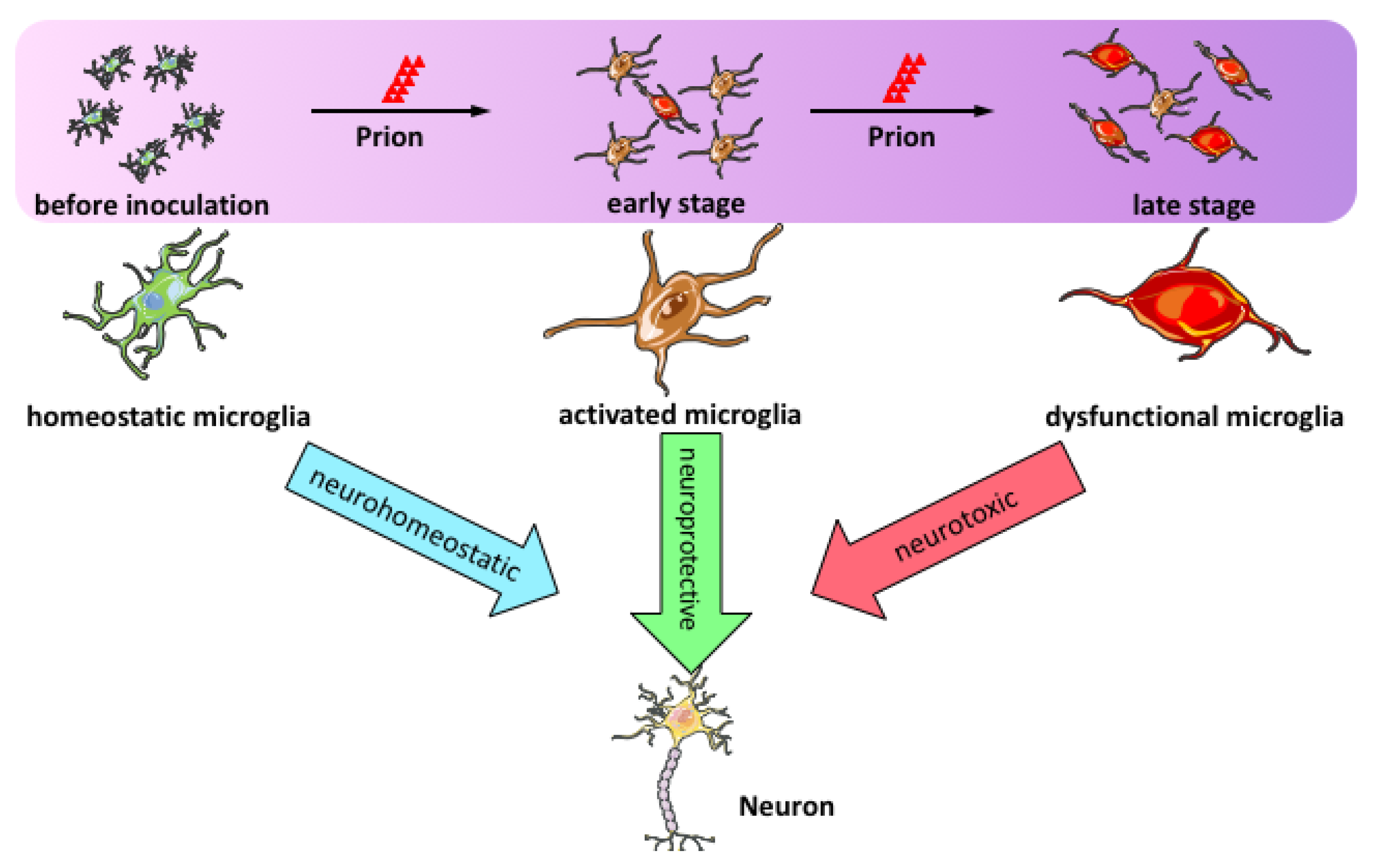
Comments
Post a Comment